RFID Technology Overview
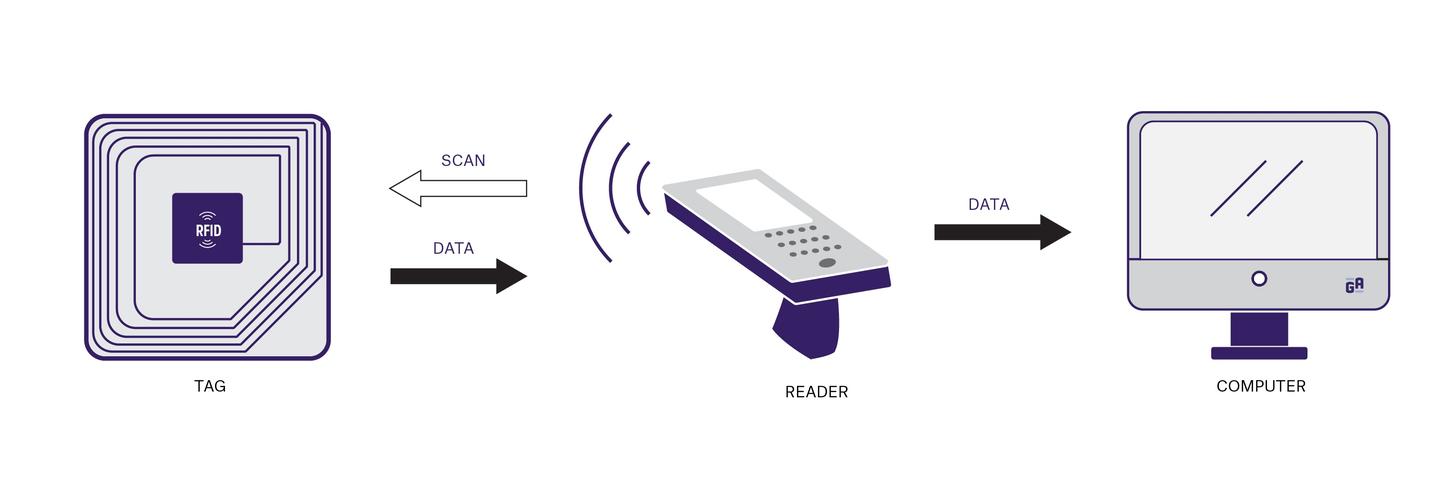
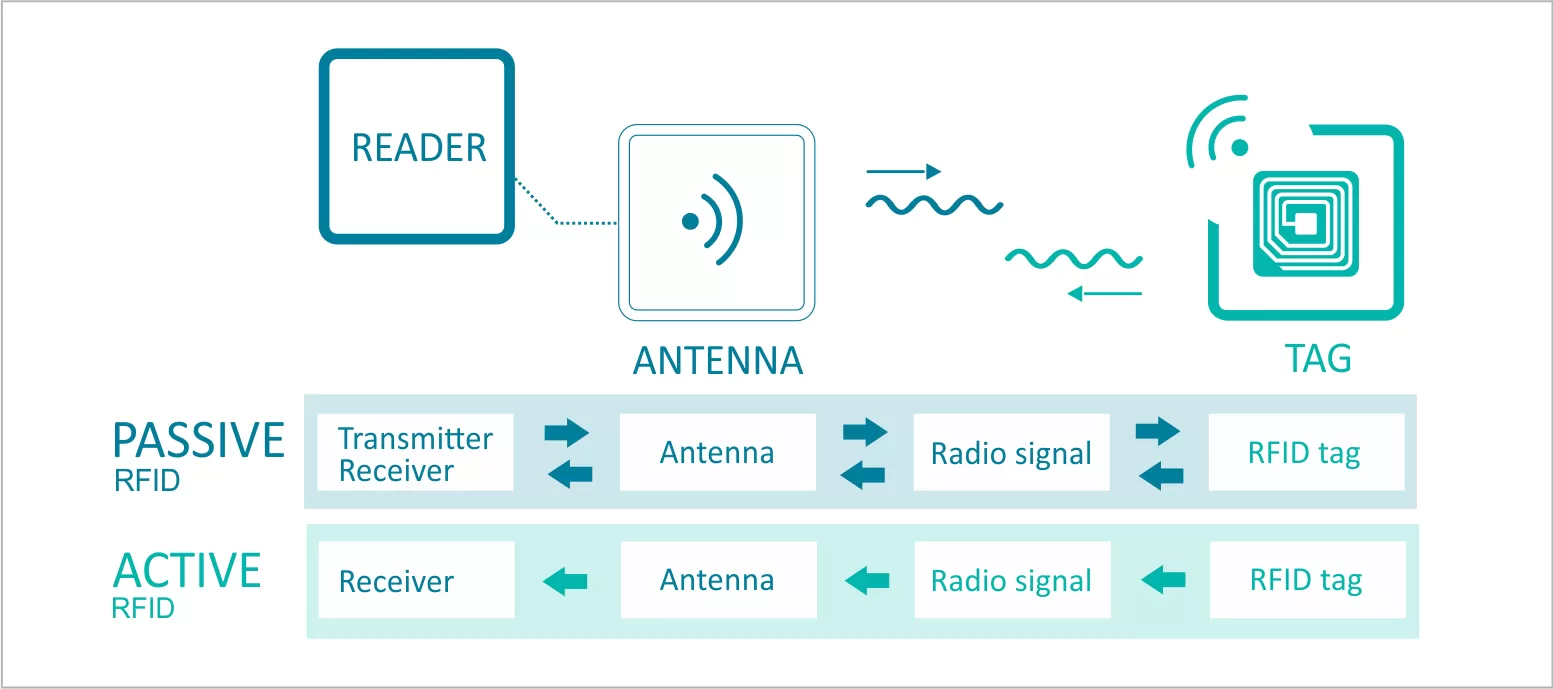
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology framework that uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to objects. RFID is primarily categorized into two types: active and passive. Each type serves different purposes and is suitable for different operating environments. A thorough understanding of their capabilities, advantages, and limitations is crucial for selecting the right RFID system.
Active RFID Tags
Active RFID tags are equipped with a power source, typically a small battery. This power source enables them to transmit signals autonomously. The presence of a battery means these tags can transmit signals at greater distances than passive tags.
Advantages of Active RFID Tags
Extended Range
Active RFID tags have a very long communication range, sometimes reaching hundreds of meters. This feature makes them ideal for tracking assets in large facilities or open outdoor environments.
Continuous Monitoring
Because active tags are battery-powered, they can support real-time asset tracking. This feature is particularly useful in dynamic environments where asset locations frequently change.
Embedded Sensors
Many active RFID tags have integrated sensors that can monitor environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. This feature is particularly useful in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food logistics, where environmental control is crucial.
Limitations of Active RFID Tags
Higher Cost
Due to the inclusion of batteries and other electronics, active RFID tags are generally more expensive than passive tags. This cost factor can be significant when deploying large-scale RFID systems.
Limited Battery Life
Battery life limits the useful life of active RFID tags. Once the battery is depleted, the tag or battery needs to be replaced, which can be labor-intensive and costly.
Larger Size
Due to the need to accommodate the battery, active tags are generally larger than passive tags. This size limits their use on smaller items.
Passive RFID Tags
Passive RFID tags differ from active tags in that they do not have an internal power source. Instead, they are powered by electromagnetic energy emitted by the RFID reader. Their compact size and cost-effectiveness make them a viable option for many applications.
Advantages of Passive RFID Tags
Cost-Effectiveness
Because passive RFID tags do not require an internal power source, their production costs are typically lower, enabling large-scale deployment without significant capital expenditures.
Smaller Size
Because passive tags do not require a battery, they are smaller and lighter, making them suitable for attachment to items with limited space.
Longer Lifespan
Because passive tags do not require a battery, they can theoretically last indefinitely, provided they are not physically damaged.
Limitations of Passive RFID Tags
Limited Read Range
Passive RFID tags have a short read range, typically only a few meters. This limitation can be a disadvantage in scenarios requiring long-distance asset tracking.
Dependence on Reader Power
They rely entirely on proximity to the reader for activation, which can limit their functionality in certain applications.
Active RFID Industry Applications
Active RFID tags are suitable for industries requiring wide-area tracking and real-time data collection:
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Real-time tracking of goods within large facilities and during transportation.
- Oil and Gas: Monitoring equipment in vast and often hazardous environments.
- Healthcare: Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) for tracking patients and high-value medical devices.
Passive RFID Industry Applications
Passive RFID tags are widely used in industries where cost-effectiveness and space are primary considerations:
- Retail: Inventory management and loss prevention by tagging items.
- Libraries: Streamlining inventory counts and inbound and outbound processes.
- Access Control: Providing secure access to facilities for employees using access cards.
Conclusion
The choice between active and passive RFID tags depends on your specific application needs. By understanding the nuances of each tag type, stakeholders can make informed decisions that optimize operational efficiency and drive business success. Whether active or passive, RFID technology has enormous potential to revolutionize the way businesses manage assets and data, making operations across all industries more intelligent and connected.