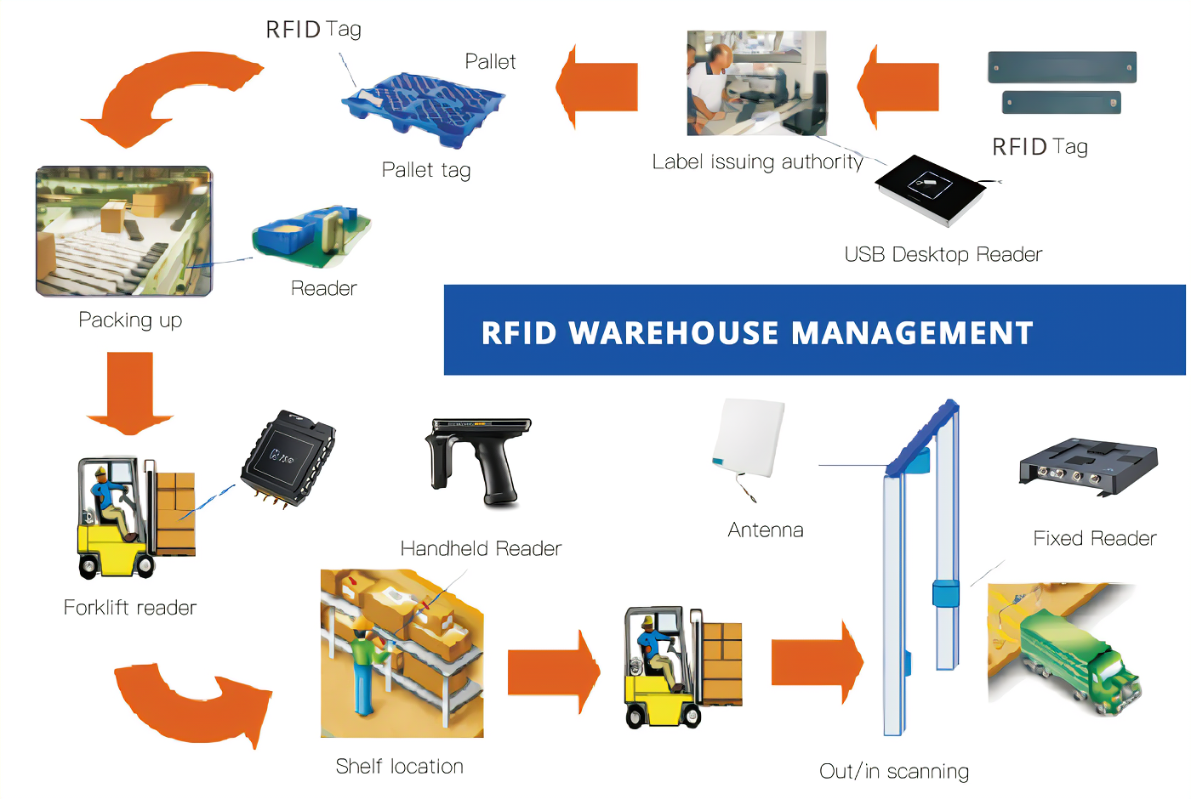
By integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, IoT devices, and RFID, companies can optimize warehousing processes and improve efficiency and accuracy. RFID plays a key role in streamlining inventory management, reducing errors, and increasing visibility. This article explores the application of RFID in smart warehousing, its associated benefits and challenges, and real-world use cases.
RFID Applications in Smart Warehousing
Improving Inventory Management
RFID provides real-time inventory tracking, enabling warehouse managers to quickly locate items and reduce search time. For example, anti-metal passive RFID tags can effectively track bulk items stacked on pallets. Retail companies use RFID for inventory counts, reducing manual labor and improving accuracy.
Automating Goods Inbound and Outbound Processes
RFID streamlines the process of moving goods in and out of the warehouse. RFID readers placed at docking stations automatically scan incoming goods and update inventory records. Similarly, outbound goods can be tracked to ensure accurate delivery to customers. This improves throughput in warehouses that handle large volumes of goods daily.
Asset Tracking and Maintenance
RFID isn't limited to inventory tracking; it can also monitor warehouse assets like forklifts, containers, and tools. Asset management RFID tags attached to machinery can provide maintenance data, such as usage hours and repair schedules, ensuring long-term efficient operations.
Real-Time Data Insights
RFID technology seamlessly integrates with warehouse management systems, providing real-time data insights. A connected RFID network provides key performance indicators, helping companies make faster and more informed decisions about inventory balancing or replenishment.

Advantages of RFID in Smart Warehousing
Improved Accuracy
Traditional inventory management methods rely heavily on manual labor and are prone to human error. RFID minimizes these errors by automating data collection and synchronization.
Increased Operational Speed
RFID scanners can process hundreds of tags simultaneously without line of sight. This capability significantly speeds up inventory counts and item tracking.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Precise tracking and faster processing speeds enable companies to efficiently fulfill customer orders. Reduced delivery delays and improved inventory visibility contribute to higher customer satisfaction and retention.
Cost Reduction
While implementing RFID requires an upfront investment, it can yield long-term cost savings. Reduced labor costs, minimized product loss, and improved efficiency make RFID a cost-effective solution for smart warehousing.
Sustainability
RFID supports sustainable practices by reducing paper-based tracking systems. Digital inventory management helps reduce waste and aligns with a company's sustainability goals.

Case Study
Cainiao Announces Full Integration of RFID Technology
Cainiao, a leading global smart logistics company, recently announced the full integration of RFID technology, becoming Hong Kong's first fully RFID-enabled freight center. Cainiao Hong Kong Easy Logistics has integrated RFID technology into every aspect of its operations. Compared to traditional freight centers, Cainiao Hong Kong Easy Logistics has increased parcel processing efficiency by approximately 30%.
Decathlon: RFID in Retail Warehousing
Decathlon, a global sporting goods retailer, has implemented RFID technology in its warehouses and stores worldwide. All products are tagged with RFID, enabling seamless inventory counting and tracking.
DHL's Smart Logistics
Logistics giant DHL uses RFID technology for asset tracking and inventory management in its warehouses. RFID tags on packages provide real-time visibility throughout the supply chain.
RFID Deployment Best Practices
Conducting a Feasibility Study
Before implementing RFID, companies should conduct a comprehensive feasibility study that considers cost, infrastructure, and operational objectives. Identifying potential bottlenecks ensures a smooth deployment.
Choosing the Right RFID Tag
A variety of RFID tags are available for different purposes, including passive, active, and semi-passive tags. Selecting the right tag for your operational needs is crucial for optimal functionality.
Conclusion
RFID is a transformative technology that can enhance smart warehouse operations. Case studies from Cainiao, Decathlon, and DHL demonstrate that despite initial costs and technical challenges, seamlessly integrating RFID into warehouse processes can deliver significant benefits, such as faster operations, reduced errors, and improved customer satisfaction.