Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology has revolutionized industries by enabling efficient asset tracking, identification, and management. However, choosing the right RFID frequency—low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), or ultrahigh frequency (UHF)—can be a challenge. This article explores the differences between these frequencies, their applications, and how to choose one based on your needs.
Understanding RFID Frequencies: LF, HF, and UHF
Low Frequency (LF) RFID (125-134 kHz)
LF RFID has a shorter operating range, typically less than 10 cm, and is known for its robustness in harsh environments.
Key Features:
-Minimal interference from water or metal, making it ideal for applications such as animal tracking and access control.
-LF has a lower data transfer rate compared to HF and UHF.
-Typically used in environments where short-range identification is sufficient for security.
Product Example:
125Khz LF T5577 RFID Hotel Key Cards
These custom hotel key cards use LF RFID technology to provide secure access control for guests. They are tamper-resistant and compatible with a variety of hotel management systems, providing enhanced security while offering customization options to enhance branding and generate revenue.

High Frequency (HF) RFID (13.56 MHz)
HF RFID offers a medium read range (up to 1 meter) and supports faster data transfer speeds than LF. It is the standard frequency for Near Field Communication (NFC).
Key Features:
-Ideal for applications that require secure data exchange, such as payment systems and ID cards.
-Widely used in libraries, public transportation, and access control systems.
-NFC-enabled for seamless integration with smartphones and other devices.
Product Example:
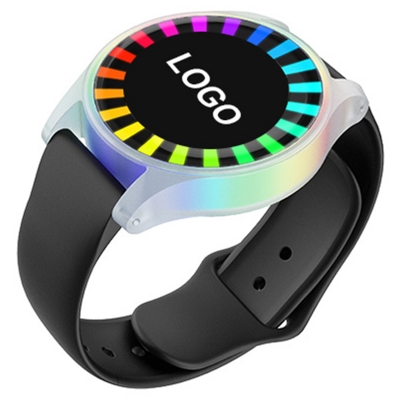
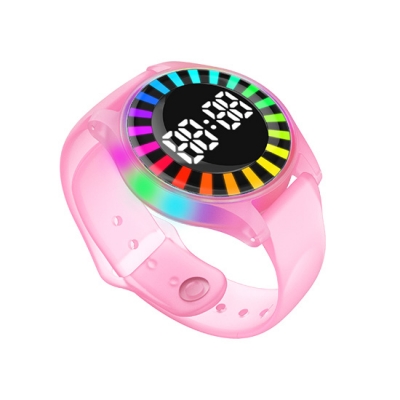
Adventure Park Customized HF LED RFID Wristbands
Combining HF RFID technology with LED lighting, these wristbands are ideal for adventure parks, and entertainment venues. With features such as magnetic charging and compatibility with access control systems, the wristbands provide a versatile solution for tracking visitors and enhancing the experience.

UHF RFID (860-960 MHz)
UHF RFID offers long-range reading (up to 12 meters or more) and the highest data rate of all RFID frequency bands.
Key Features:
-Ideal for applications that require scanning multiple items simultaneously, such as inventory management and supply chain tracking.
-Vulnerable to liquids and metals, but performs well in open environments.
-Compliant with global standards such as EPC Global Class 1 Gen 2 and ISO-18000 6C.
Product Examples:
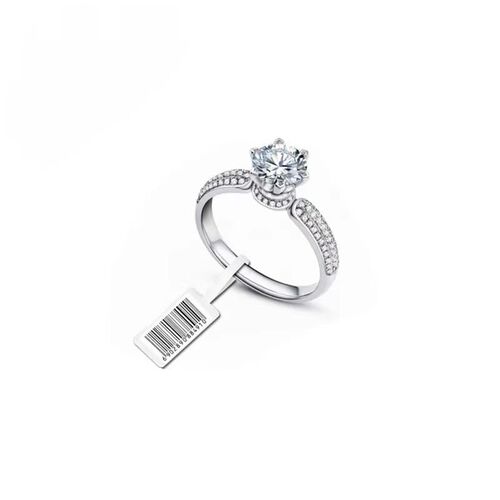
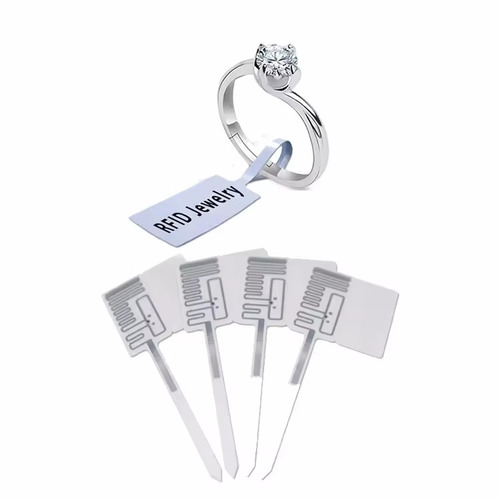
Custom Printed UHF Anti-Theft RFID Jewelry Tags
Designed for jewelry management, these UHF RFID tags perform well in harsh radio frequency (RF) environments. With anti-collision features, anti-tamper design, and global frequency compatibility, they ensure reliable performance and higher read rates even in dense environments.


Choosing the Right RFID Frequency
Application-Specific Considerations
Access Control: High-Frequency (HF) RFID is ideal for secure, mid-range applications, such as hotel room cards and wristbands.
Inventory Management: Ultra-High-Frequency (UHF) RFID excels at long-range, high-speed scanning in retail and logistics.
Harsh Environments: Low-Frequency (LF) RFID is the best choice for applications involving water or metal, such as animal tracking.
Environmental Considerations
Consider the presence of liquids, metal, and other potential sources of interference. Low-Frequency (LF) RFID performs well in harsh conditions, while Ultra-High-Frequency (UHF) RFID is better suited for open environments.
Data Transfer and Security Needs
HF RFID enables secure data exchange and is suitable for payment systems and ID documents. UHF RFID offers high-speed data transfer and is ideal for supply chain management.
Cost and Scalability
Low-Frequency systems are generally more affordable, while UHF systems offer superior performance but are more expensive. Evaluate your budget and scalability requirements before making a decision.
Future Trends in RFID Technology
The RFID industry is evolving rapidly, with hybrid systems incorporating multiple frequencies and integrating advanced features such as IoT connectivity. Products such as the “Custom HF LED RFID NFC Wristband” and “Custom Printed UHF Anti-Theft RFID Jewelry Tags” represent the next generation of RFID solutions, offering versatility, reliability, and enhanced functionality.
Conclusion
Choosing the right RFID frequency depends on your specific use case, environmental conditions, and performance requirements. Whether you need the robustness of low frequencies, the versatility of high frequencies, or the speed and range of UHF, there is an RFID solution that will meet your needs.