
RFID (radio frequency identification) technology has revolutionized library operations by automating processes such as book tracking, inventory management, and security. Libraries around the world are adopting RFID to enhance the user experience and streamline workflows. This article explores the technical aspects, benefits, challenges, and practical applications of RFID in libraries, and introduces some innovative products that can enhance library management systems.
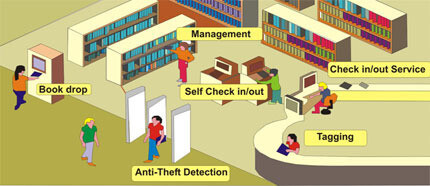
A library's RFID system consists of three main components: tags, readers, and software. RFID tags are embedded in books or other resources and store unique identifying data. Readers, placed at checkout counters or entrances, capture this data via radio waves. The software integrates with the library's management system to process and update the information in real time.
For example, the RFID Library Tag with 3M Self-Adhesive Label is a high-quality solution that can store detailed book information. Its high-capacity chip supports contactless data reading and writing, with a read range of 0.05 to 1.2 meters, making it ideal for efficient library operations.
RFID systems in libraries typically operate at a high frequency (13.56 MHz) with a read range of up to 1 meter. This ensures accurate and fast scanning, and is immune to interference. Examples include the "13.56 MHz Library Tag," which is reliable and easily integrated with existing library infrastructure.
RFID significantly reduces the time required for tasks such as borrowing, storage, and inventory management. A study by the University of Hong Kong found that RFID systems reduced book processing time by 40%. RFID also minimizes human error and ensures accurate data entry and tracking.
RFID tags can be integrated with anti-theft systems, triggering an alarm if a book is removed without authorization. The Library Management RFID Anti-Theft Tag is an excellent solution that is standard and compatible with all UHF RFID readers. Its strip design makes it easy to attach to the seams of books, improving security and management efficiency.
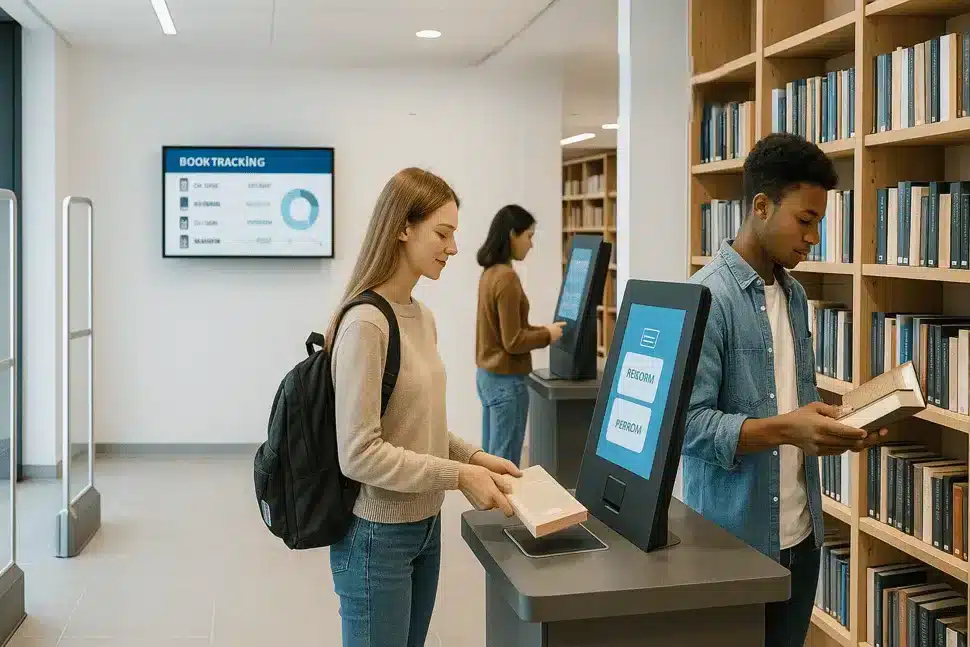

RFID-enabled self-service kiosks allow users to independently borrow and return books, reducing wait times and improving the overall user experience.
RFID tags can be used to track users' reading habits, raising privacy concerns. Libraries must implement strict data protection policies to address these issues. The EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) provides a framework for protecting user data.
RFID systems can face challenges in metallic or liquid environments, as metal or liquid interferes with radio waves. Libraries must carefully plan tag placement and reader location to mitigate these issues.
The National Library of Singapore implemented RFID technology in 2015, which has reduced checkout times by 30% and increased inventory accuracy by 20%. The system also enabled the library to introduce self-service kiosks, enhancing the user experience.
The University of Hong Kong implemented RFID technology in 2018, which has reduced book processing time by 40% and staff workload by 15%. The system also improved security and reduced theft by 35%.
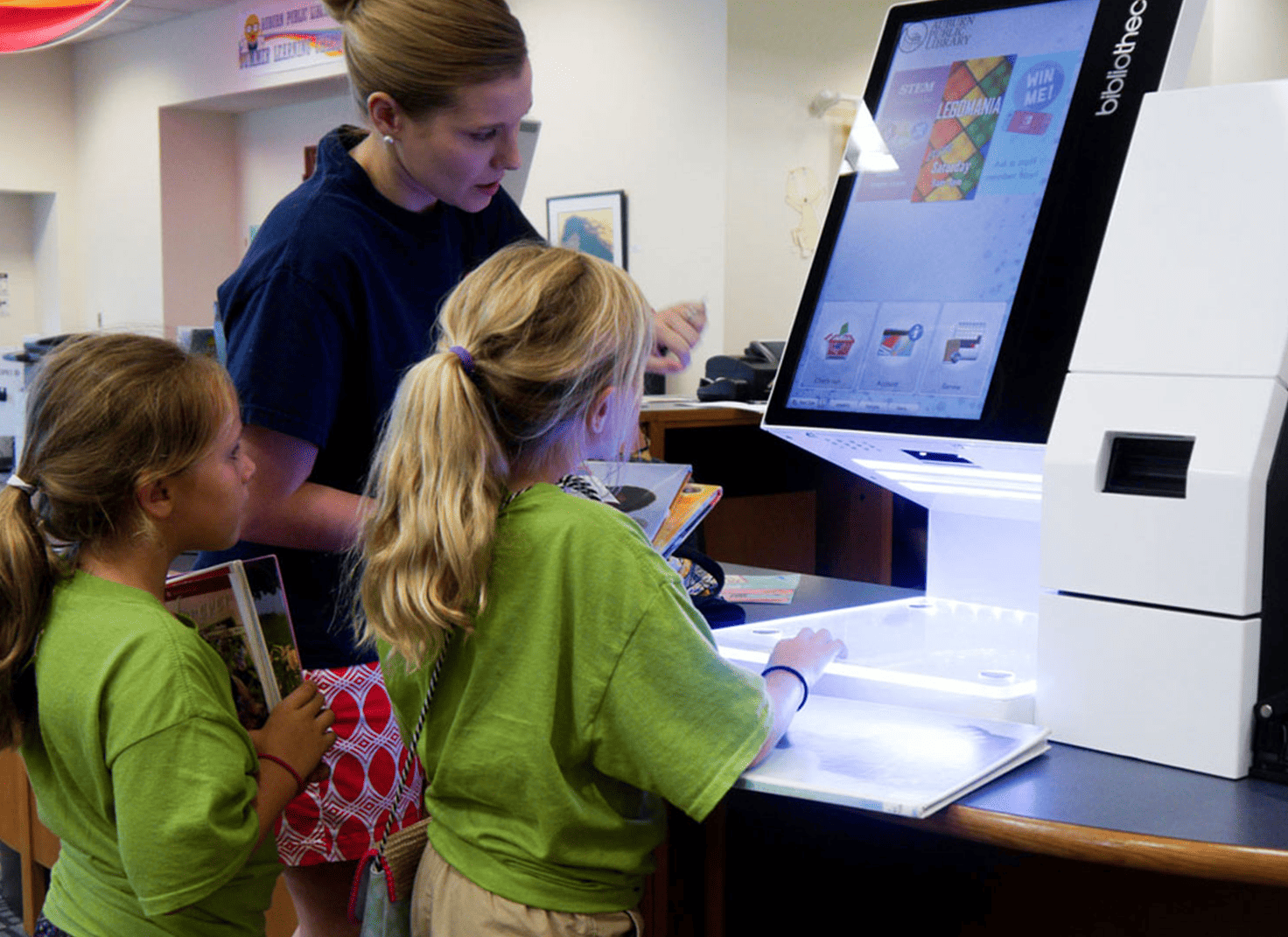

The New York Public Library integrated RFID technology in 2020, which has reduced theft by 50% and increased user satisfaction by 25%. The library also reported significant improvements in inventory management and resource allocation.
RFID systems are increasingly integrated with AI and IoT technologies to enable predictive analytics and intelligent resource management. For example, AI can analyze borrowing patterns to optimize book placement and staffing.
Manufacturers are developing environmentally friendly RFID tags made from biodegradable materials. These tags maintain performance while reducing environmental impact, which aligns with libraries' sustainability goals.
RFID systems can provide detailed insights into user behavior, helping libraries tailor services to community needs. For example, data on popular categories can guide collection development and event planning.
With advancements in artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT), RFID systems are evolving to further enhance library resource management and service delivery. By adopting RFID, libraries can stay ahead in the digital age and better serve their communities. RFID technology not only streamlines workflows but also ensures security, accuracy, and sustainability in library management.
Chat NOW
Scan to wechat :

Scan to Whatsapp :
