Introduction to RFID in Retail
Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology has revolutionized the retail industry by enabling seamless inventory management, enhancing the customer experience, and improving operational efficiency. RFID uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, providing real-time data that retailers can leverage to offer personalized services. This article combines case studies, technical insights, and industry data to explore how RFID is transforming retail through personalization.
How RFID Works in Retail
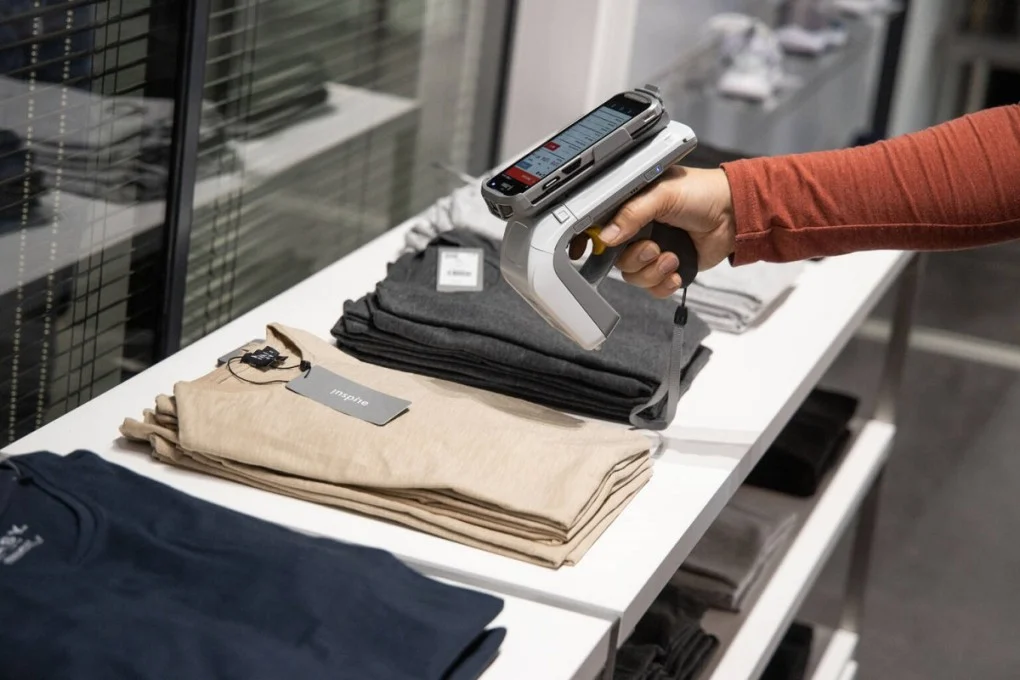
RFID systems consist of three key components: tags, readers, and software. Tags are embedded in products and store unique identifiers. Readers capture data from tags via radio waves, and software processes this data to derive actionable insights. Unlike barcodes, RFID does not require line-of-sight scanning, enabling faster and more accurate inventory tracking. For example, a single RFID reader can scan hundreds of items simultaneously, reducing manual processing and errors.
Advantages of RFID Personalization
RFID enables retailers to deliver customized experiences by collecting and analyzing customer data in real time. Key benefits include:
Enhanced Customer Insights
RFID can track customer interactions with products, such as the items they select or try on, providing valuable behavioral data.
Personalized Recommendations
By combining RFID data with AI algorithms, retailers can recommend products based on individual preferences.
Efficient Checkout Processes
RFID-enabled self-checkout systems reduce wait times and increase customer satisfaction.
Case Study: Zara's RFID Implementation
Global fashion retailer Zara successfully implemented RFID technology to improve operational efficiency. By tagging every item in its stores, Zara achieved 98% inventory accuracy and reduced out-of-stocks. The technology also enabled personalized services, such as notifying customers when their desired items were in stock. This resulted in a 10% increase in sales and improved customer retention.
Challenges and Solutions for RFID Applications
While RFID offers significant advantages, its implementation also presents challenges:
High Initial Cost
RFID tags and infrastructure require a significant investment. However, long-term benefits, such as reduced labor costs and increased sales, often outweigh the initial investment.
Privacy Concerns
Consumers may be concerned about data misuse. Retailers must ensure transparency in their data policies and comply with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Technical Limitations
RFID signals can be interfered with by metal or liquids. Advanced tags and readers are now available to mitigate these issues.
Future Trends in RFID Personalization
The future of RFID in retail lies in its integration with emerging technologies:
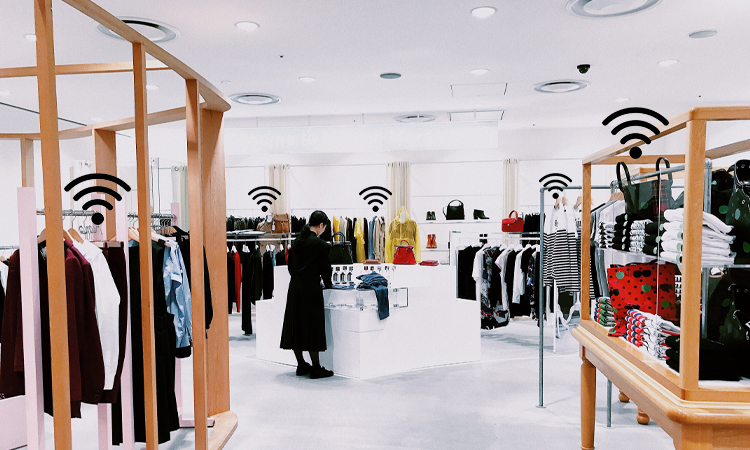
The Internet of Things and Smart Stores
RFID will work in tandem with IoT devices to create a fully automated, personalized shopping environment.
Augmented Reality (AR)
The combination of RFID and AR can enable virtual try-ons and interactive product displays.
Blockchain Data Security
Blockchain can enhance RFID data security, ensuring customer privacy and trust.
Conclusion
RFID technology is reshaping the retail industry, providing personalized services, improving the customer experience, and driving business growth. Despite numerous challenges, the benefits of adopting RFID are undeniable. As the technology continues to evolve, retailers who adopt RFID will gain a competitive advantage in the market. By leveraging real-time data and innovative solutions, the future of retail will be more personalized, efficient, and customer-centric than ever before.