Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) smart cards are a key technology in modern commercial and consumer environments. Since the late 1990s, their use has surged due to advances in data encryption, miniaturization, and cost-effectiveness.
Access Control and Security
RFID smart cards are ubiquitous in access control for businesses, educational institutions, and government agencies. System administrators can instantly assign or revoke access rights, track access logs, and respond to security breaches in real time. When combined with PIN codes, biometrics, or mobile authentication apps, RFID smart cards enable multi-factor authentication.
Contactless Payments
RFID-enabled contactless payment cards, particularly those compliant with the EMV standard, have become widely used in the financial industry. Users simply hold their card near a compatible terminal to complete a transaction; payments are securely processed in seconds.
Public transportation systems around the world have adopted RFID smart cards for fares and ticketing. Notable examples include London's Oyster card and Hong Kong's Octopus card, both of which enable instant payments, streamlining commuting.
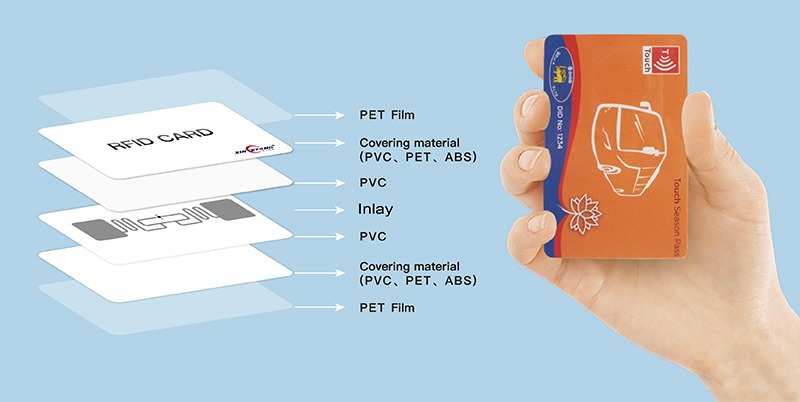
Education and Campus Management
RFID smart cards are widely used in educational institutions for identification, attendance, and access control. Each card is linked to personal information, streamlining check-in, library borrowing, and cafeteria payment processes.
Campus facilities can be reserved using RFID smart cards. The reservation system provides time-limited access and tracks equipment usage, reducing duplicate bookings and theft. This integration streamlines campus operations and facilitates data-driven infrastructure investment decisions.
Library Management
RFID smart cards streamline library workflows, automating check-in/out processes and enabling users to borrow or return multiple books in seconds. Inventory audits, typically labor-intensive, can be completed in hours rather than days, improving collection management and reducing losses.
Hotels & Leisure
Hotels are replacing magnetic stripe room cards with RFID smart cards to improve guest convenience, durability, and security. RFID-enabled hotel room cards are more resistant to demagnetization and cannot be read by off-the-shelf equipment, reducing the risk of unauthorized duplication.
RFID cards can be integrated with mobile apps for digital check-in, room selection, and a personalized guest experience. Some resorts offer waterproof RFID wristbands or cards for seamless all-inclusive payment and facility access.
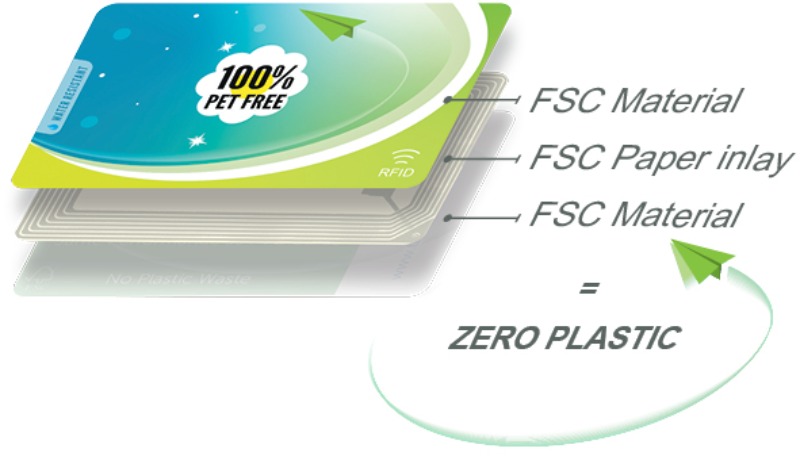
Government & Public Services
Many countries have adopted RFID-enabled ID cards and passports to enhance security and streamline border control. These documents are embedded with contactless chips that store biometric data, travel history, and digital signatures.
Governments around the world issue RFID-enabled social security, health insurance, and welfare cards. Because only registered users with valid smart cards can access healthcare benefits, fraudulent claims and identity theft are effectively curbed.
Automotive and Transportation
RFID smart cards and tags are the foundation of electronic toll collection systems worldwide. Vehicles equipped with RFID tags or cards can pass through dedicated lanes, and tolls are automatically deducted from prepaid accounts.
These systems can reduce fuel consumption, reduce idling emissions, and ease traffic congestion.
Corporate fleets, residential complexes, and city parking lots use RFID smart cards to control vehicle access. Automated parking lots combine RFID card access with payment and reservation systems, ensuring only authorized vehicles can enter restricted areas.
Environmental Sustainability of RFID Smart Cards
Early RFID smart cards raised environmental concerns due to the use and disposal of plastics, but recent innovations include biodegradable substrates, recyclable chip components, and energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
The transition to multi-use RFID smart cards can reduce resource consumption and plastic waste.
Challenges and Future Directions
Scaling RFID smart card solutions requires adherence to global standards, backward compatibility, and a flexible system architecture. Interoperable platforms, open APIs, and collaborative governance initiatives are shaping the landscape for seamless integration.
The initial deployment cost depends on the scale and complexity of the application. However, case studies consistently demonstrate a rapid return on investment through improved operational efficiency, reduced errors, and data-driven decision-making.
Future trends include the increasing adoption of hybrid biometric RFID cards for enhanced authentication and AI-driven real-time analytics based on RFID-collected data.

Conclusion
RFID smart cards are a versatile, scalable, and future-proof solution suitable for a wide range of industries. Applications range from secure access and payment to healthcare, logistics, and public services.
Investing in RFID smart cards will provide strategic advantages for businesses. Continued integration with emerging technologies will further enhance the potential of RFID smart cards as a foundational tool for intelligent, connected systems.
Chat NOW
Scan to wechat :

Scan to Whatsapp :
